Learning Objectives
- At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to:
- Explain the mechanism of determination of loudness
- Describe the auditory pathway
- Explain the process of determination of direction from which sound is coming
- Explain various hearing Abnormalities
Review

Impedance matching?
Attenuation reflex.
What is the sensory organ of hearing?
How does organ of corti work?
What is the role of tectorial membrane in organ of corti?
Place principle.






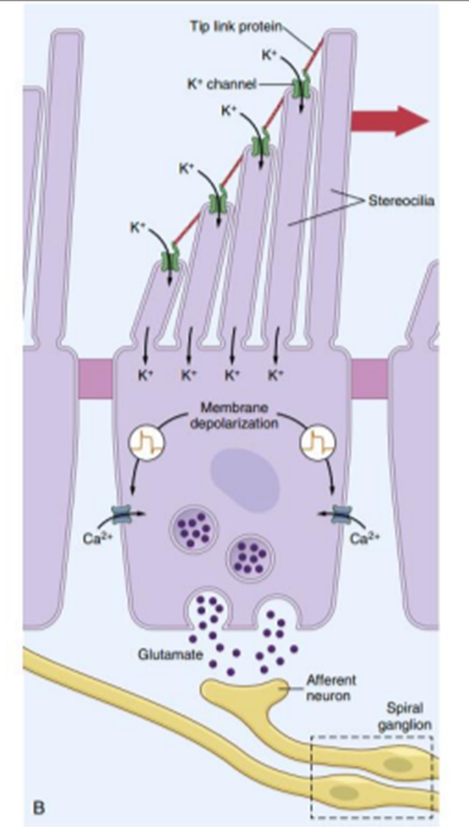
Endo cochlear Potential
Difference of +80 mV between
Endolymph and Perilymph
Positivity inside scala media due to
Potassium ions in endolymph
The negative potential inside hair cell :
-70mV with respect to perilymph
-150mv with respect to endolymph
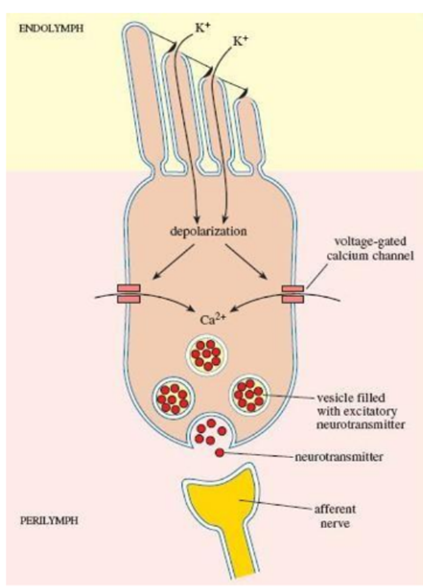
Determination of loudness
Determination of Loudness
Amplitude and intensity of vibrations increase causing:
- Nerve endings are excited at a rapid rate
- More hair cells are stimulated, causing spatial
summation - Outer hair cells are stimulated
Auditory Pathway


Auditory Cortex
Lies on the supra-temporal
plane of the superior temporal
gyrus but also extends onto
the lateral side of the temporal
lobe
- Has two subdivisions:
- Primary Auditory Cortex
- Secondary/ Association

Tonotopic Map

Functions of Auditory Cortex
- Discrimination of:
- Tonal and sequential sound
patterns - Sound frequencies
- Noise and true speech
- Direction of sound
- Meaning of sound
What will happen ifprimary auditory cortex is
destroyed?
and
What will happen if secondary auditory cortexis
destroyed?
Determination of Direction of Sound

Determination of the Direction
- Time lag between the entry of sound in both ears
- Difference between the intensities of sound in both ears
- Neural Mechanisms
Determination of the Direction
- Time lag between the entry of sound in both ears
- For frequencies < 3000cycles/ sec
- Difference between the intensities of sound in both ears
- For frequencies > 3000cycles/ sec
Determination of the Direction
- Medial Superior Olivary Nucleus• Lateral Superior Olivary Nucleus
- Detect the time lag between the acoustic signals
- Detects the direction from which sound is coming by comparing the difference in intensities of sound
Hearing Loss

Hearing loss/ Deafness
Sensory-neural :
caused by impairment of the cochlea, the auditory nerve, or the
central nervous system circuits from the ear
Conductive:
caused by impairment of the physical structures of the ear that
conduct sound itself to the cochlea

