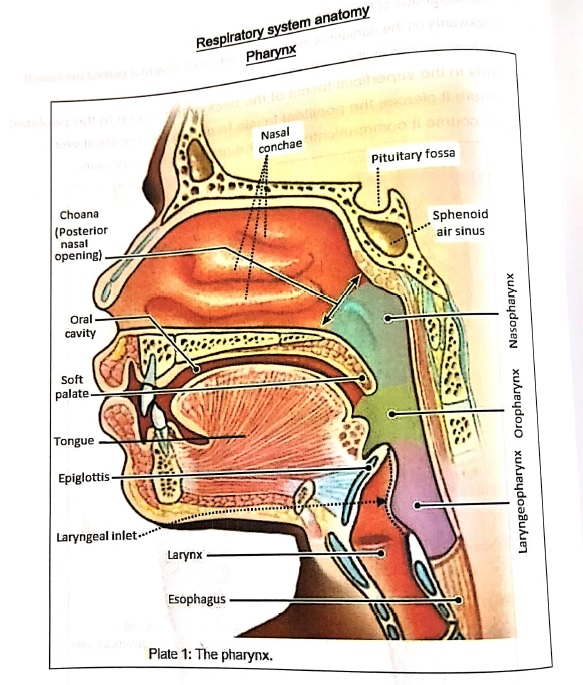
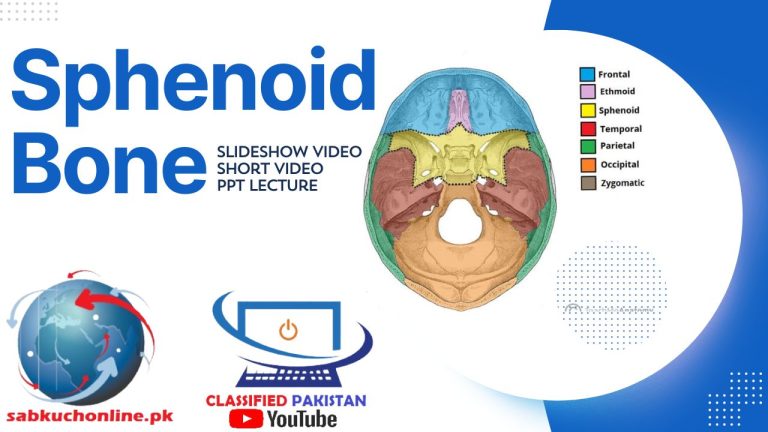
Categories
- 943All
- 4Advance Imtiaz Shahid
- 12AIOU pdf books
- 49Anatomy Books
- 156Anatomy Lectures PowerPoint
- 222Anatomy Notes
- 16Biochemistry Books
- 42Biochemistry PowerPoint Slides
- 31Cambridge Books
- 13CARAVAN Books
- 35Clinical pdf books
- 7Computer Short Course Books
- 4Dentistry pdf Books
- 38Dogar Books
- 4English Course
- 6Forensic Medicine Books
- 11Forensic Medicine Slides
- 15Ghazali Books & Notes
- 0Graduate Books & Notes
- 1Histopathology pdf books & Notes
- 5How To
- 85Intermediate Books & Notes
- 2Internal Medicine pdf books
- 21Jahangir's WT Books
- 7KIPS Books
- 0Master Books & Notes
- 81Matric Books & Notes
- 2Medicine pdf books
- 8Nursing pdf books
- 53Other Notes
- 7Oxford Books & Notes
- 10Pathology Books
- 1Pediatrics pdf books
- 11Pharmacology Books
- 1Pharmacology Slideshow
- 17Physiology Books
- 130Physiology PowerPoint Slides
- 2Surgery pdf books
- 2VU PDF Books