•The urinary bladder, a hollow viscus with strong muscular walls, is characterized by its distensibility.

•The bladder is a temporary reservoir for urine, and varies in size, shape, position, and relationships according to its content

•The urinary bladder is situated immediately behind the pubic bones, within the pelvis.
•It is separated from these bones by retropubic space and lies mostly inferior to the peritoneum, resting on the pubic bones anteriorly and the prostate (males) or anterior wall of the vagina (females) posteriorly.
•In the adult, the empty bladder lies entirely within the pelvis. As the bladder fills, its superior wall rises up into the hypogastric region.
•In infants and young children, the urinary bladder is in the abdomen even when empty.

Gross features
•The empty bladder is pyramidal, having an apex, base, neck, superior surface, and two inferolateral surfaces.
APEX:
•The apex of the bladder points anteriorly and lies behind the upper margin of the symphysis pubis. It connects to the umbilicus by the median umbilical ligament.

BASE:
•The base of the bladder is shaped like an inverted triangle and faces posteroinferiorly
•The two ureters enter the bladder at each of the upper corners of the base, and the urethra drains inferiorly from the lower corner of the base.

•Inside, the mucosal lining on the base of the bladder is smooth and firmly attached to the underlying smooth muscle coat of the wall.
•The smooth triangular area between the openings of the ureters and urethra on the inside of the bladder is known as the trigone.
•The upper part of the base of the bladder is covered by peritoneum, which forms the anterior wall of the rectovesical pouch.

INFEROLATERAL SURFACE:
•The inferolateral surfaces of the bladder are cradled between the levator ani muscles of the pelvic diaphragm and the adjacent obturator internus muscles above the attachment of the pelvic diaphragm
•In front they are related to the retropubic pad of fat and the pubic bones.

SUPERIOR SURFACE:
•The superior surface is slightly domed when the bladder is empty, it balloons upward as the bladder fills.
•Superiorly, it is covered with peritoneum and is related to coils of ileum or sigmoid colon.
•When the bladder is filled, the peritoneal covering is peeled off the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall so that the bladder comes into direct contact with the anterior abdominal wall.

NECK:
•The neck o f the bladder surrounds the origin o f the urethra at the point where the two inferolateral surfaces and the base meet.
•The neck is the most inferior part of the bladder and also the most “fixed” part.
•The neck of the bladder is held in position by the puboprostatic ligaments in the male, these are called the pubovesical ligaments in the female.

INTERNALLY:
•The mucous membrane of the greater part of the empty bladder is thrown into folds that disappear when the bladder is full. Except at the area of trigone.
•The superior angles of the trigone correspond to the openings of the ureters, and the inferior angle to the internal urethral orifice.
•The ureters pierce the bladder wall obliquely, and this provides a valvelike action, which prevents a reverse flow of urine toward the kidneys as the bladder fills.

- The trigone is limited above by a muscular ridge, which runs from the opening of one ureter to that of the other and is known as the interureteric ridge.
- The uvula vesicae are a small elevation situated immediately behind the urethral orifice, which is produced by the underlying median lobe of the prostate.
- The muscular coat of the bladder is composed of smooth muscle and is arranged as three layers of interlacing bundles known as the detrusor muscle.
- The circular component of the muscle coat is thickened at the neck of the bladder to form the sphincter vesicae (internal urethral sphincter).

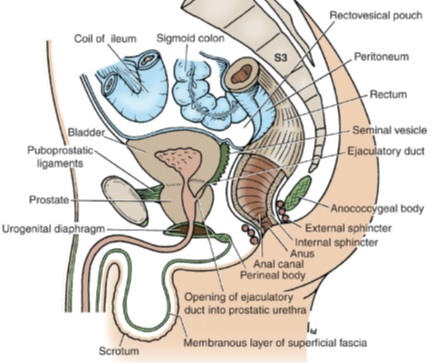
IN THE MALES:
- The two vasa deferentia lie side by side on the base of the bladder and separate the seminal vesicles from each other.
- The upper part of the base of the bladder is covered by peritoneum, which forms the anterior wall of the rectovesical pouch. The lower part of the base is separated from the rectum by the vasa deferentia, the seminal vesicles, and the rectovesical fascia.

IN THE FEMALES:
- Because of the absence of the prostate, the bladder lies at a lower level than in the male pelvis, and the neck rests directly on the upper surface of the urogenital diaphragm.
- The base is separated from the rectum by the vagina. The superior surface is related to the uterovesical pouch of peritoneum and to the body of the uterus.

BLOOD SUPPLY

CLINICALS
•Urinary retention
•Suprapubic aspiration
•Cystoscopy
•Bladder injury