RETINA
Light sensitive portion of the eye
Contains cones for color vision
Contains rods for night vision
Contains neural architecture
Light must pass through the neural elements to
strike
The light sensitive rods and cones
LIGHT ADAPTATION
Bright light for some time (hrs)
MECHANISMS
Photosensitive chemicals in rods and cones will be
reduced to retinals and opsins
Retinals to Vitamin A
concentration of photosensitive chemicals reduced
- Change from rod to cone
vision - Constriction of pupil
Less light enters - Neural adaptation
Diminution of signals
DARK ADAPTATION
Darkness for a long time
Retinals and opsins back to light sensitive pigment
Vitamin A back to retinal
Increase in light-sensitive pigments
When person is exposed to total darkness
After remaining in light for several hours
Sensitivity of the retina—- increased
Process by which one can see in dim light
Maximum adaptation time
very low— on entering the darkness
1 min—-10 fold
20 min—–6000 fold
40 min—-25,000 fold
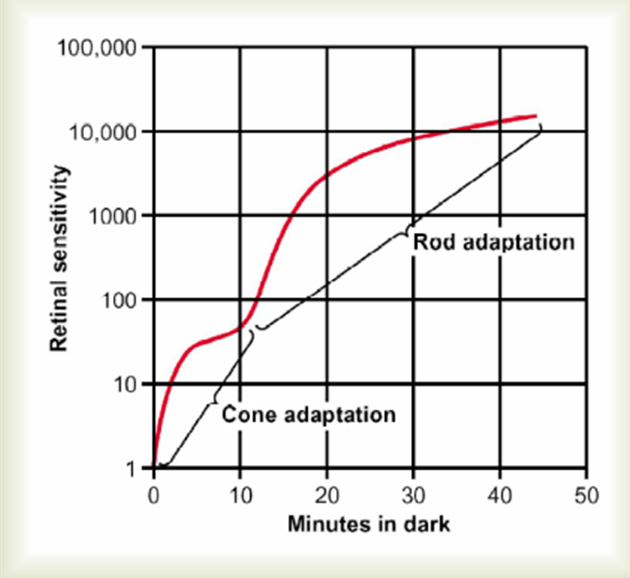
Dark adaptation curve
Adaptation of the cones
Early portion of the curve
Adaptation occurs four times more rapidly in
cones than in rods
Less level of sensitivity—Cease adapting after a few
minutes
Dark adaptation curve
Adaptation by rods
slow adaptation
More sensitive—Continue to adapt for
minutes/hours
Rods summate to increase their sensitivity
Convergence of 100 or more rods onto a single
ganglion cells in the retina
Other Mechanisms of Adaptation
Change in pupillary size
Pupil dilate more light enters
Adaptation of 30 fold— sec
Neural adaptation
Enhancement of signals
Degree of adaptation is few fold
Importance of Dark and Light Adaptation
Adaptation—-500,000 to 1 million times
The detection of images on the retina is a function
of discriminating between dark and light spots.
Registering of images by retina
Detection of dark and light spots
Receptors respond to lighter areas but not to darker
areas
Enter the sun from a movie theater, even the dark
spots appear bright leaving little contrast
Entire visual image is bleached
Enter darkness from light, the sensitivity of retina is
so slight—light spots are not light enough to
register (cannot excite the retina)
After dark adaptation the light spots begin to
register
Eyes can function in
Bright sunlight— light adaptation
Star light—dark adaptation
