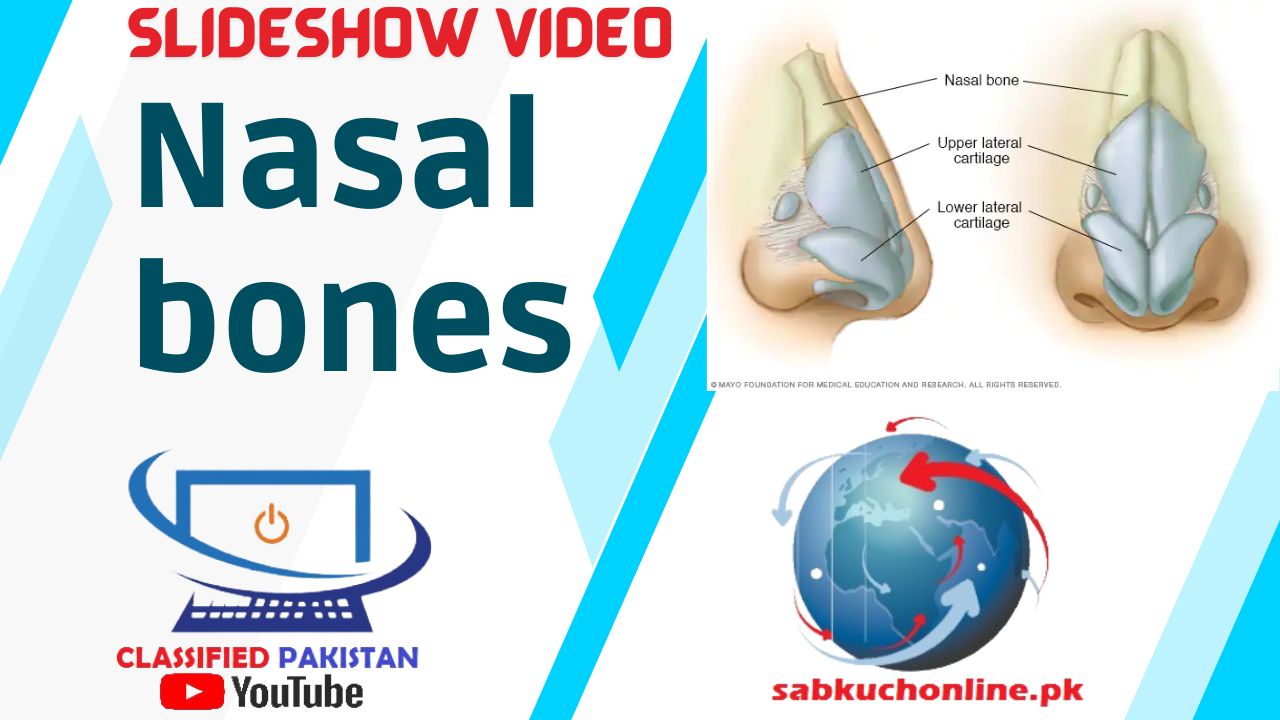
The nasal bones are two small, rectangular-shaped bones that form the bridge of the nose, helping to shape the upper part of the nasal cavity. Here are some key points about the nasal bones:

- Location: The nasal bones are situated at the midline of the face, between the frontal bone superiorly and the maxillary bones laterally. They form the bony framework of the upper part of the nose.
- Shape and Structure: The nasal bones are relatively flat and thin, and they articulate with each other at the midline to form the bridge of the nose. The nasal bones also articulate with the frontal bone superiorly and the maxillary bones laterally.
- Function: The primary function of the nasal bones is to provide structural support for the upper part of the nose and to help maintain the shape and appearance of the external nose.
- Articulations: The nasal bones articulate with several other facial bones:
- Superiorly, they articulate with the frontal bone at the frontonasal suture.
- Laterally, they articulate with the maxillary bones at the nasomaxillary sutures.
- Variation: The size and shape of the nasal bones can vary among individuals, contributing to the unique characteristics of their noses. These variations are a factor in the diversity of human facial features.
- Fractures: Due to their prominent position on the face, the nasal bones are vulnerable to injury, particularly during facial trauma. Nasal bone fractures are relatively common and can lead to changes in the shape and alignment of the nose.
The nasal bones are an important part of the facial skeleton, contributing to both the aesthetic and functional aspects of the human nose. They work in conjunction with other facial bones to create the overall structure of the nose and play a role in respiration by supporting the nasal cavity.