Flashes and Floaters
Introduction
- Light-sensitive portion of the eye
- Contains
- Cones—for color vision
- Rods– for black and white vision and vision in dark
- After excitation of photoreceptors signals are transmitted from retina
to optic nerve ending in cerebral cortex

The Fovea Centralis
- Location– slightly below and on one side of the optic disc
- Found in the centre of a shallow depression or pit (the macula lutea)
- Fovea– minute area in the center of retina i.e. slightly larger than 1
square millimeter - Capable of acute and detailed vision
- Central fovea– 0.3 mm in diameter
- Entirely composed of cones
The Fovea Centralis
- Specialized structure of these cones providing clear detail of the image
- Foveal cones
- long and slender bodies, in the foveal region
- Peripheral retina has cones with fat bodies
- Fovea also contains blood vessels, ganglion cells and inner nuclear cell
layer - Arrangement is made in a manner that light passes unimpeded to reach
the cones - Only cones are present at the fovea which have individual connections with
the bipolar and ganglion cells
Peripheral Retina
- No cones in the peripheral retina, but only rods
- Rods here are also shorter and wider than in the central retina.
- Receptive fields at the periphery are very large with many rods
converging onto one ganglion cell.
The Rods and Cones
- Photo receptors present in the outer
nuclear layer i.e. Receptor Layer of
Retina - Human receptor layer consists of
approximately 120 million rods and 6
million cones arranged side by side. - The distribution of these
photoreceptors varies across the
surface of the retina.

sensitive pigments.
- Roads and cones contain light sensitive pigments
- Each photoreceptor consists of an
outer segment which contains
hundreds of thin plates of
membrane (lamellae or discs). - The outer segment is connected
by a cilium to an inner segment
which contains a nucleus. - Rods are about 500 times more
sensitive to light than cones - cones are responsible for color
vision.

Structure of Rod/Cone
• The light-sensitive photochemical is found in the outer segment.
- In rods, this is rhodopsin • In cones, it is one of three “color” photochemicals, (color pigments) • Function same as rhodopsin except for differences in spectral sensitivity
Discs/Lamellae of Rods and Cones
- Large numbers of discs are
present in the outer segments of
the rods and cones. - Each of the discs is an infolded
shelf of cell membrane. - There are as many as 1000 discs
in each rod or cone.

Properties of Rods and Cones

Rhodopsin and Color Pigments
- Conjugated proteins.
- Present in the membranes
of the discs in the form of
transmembrane proteins. - These Pigment proteins
constitute about 40 per cent of
the entire mass of the outer
segment.

Pigment Layer of the Retina
- Black pigment melanin
- Prevents light reflection through out the globe of the eye ball
- Clear vision
- It stores large amount of vitamin A that is an important precursor of
photosensitive chemicals of rods and cones

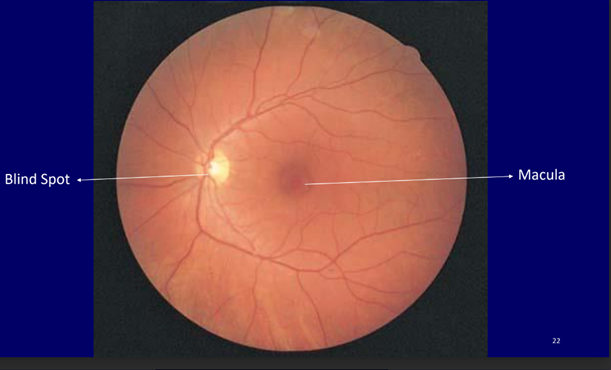
Optic Disc
- Point at which axons leave the eyeball and join the optic nerve
- Arteries enter and veins leave the retina at the optic disc.
- There are no photoreceptors at optic disc
- Also known as ‘blind spot‘
- It is a pinky-yellow oval, approximately 2mm in diameter

Pigment Layer of the Retina
- Melanin pigment layer is absent in albino
- Light reflected in all directions inside the eye ball by unpigmented
surfaces of the retina & sclera - Light excites many receptors
- Visual acuity of albinos is badly affected 20/100 to 20/200.
Retinal Detachment
Injury to the eyeball
- Fluid or blood may be collected between the neural retina and the
pigment epithelium.
Cause: - Contracture of fine collagenous fibrils in the vitreous humor
- These fibrils pull the retina toward the interior of the globe
The detached retina can resist degeneration for days because of:
1.Diffusion across the detachment gap
2.Independent blood supply by the Retinal artery
(Early surgical placement may save the permanent loss of vision)
Retinal Detachment


Rhodopsin Visual Cycle
- Outer segment contains 40% photopigment– rhodopsin/visual purple
- Combination of retinal and scotopsin
- Retinal– 11-cis type
- Readily binds to scotopsin

Rhodopsin Visual Cycle
- Rhodopsin decompose when light falls on retina
- Rhodopsin decompose in fraction of a second
- Photoactivation of electrons in retinal portion of rhodopsin
- cis form of retinal is converted into all-trans form
- All trans form has no binding sites for scotopsin
- Decomposed into retinal and scotopsin
Rhodopsin Visual Cycle
- First product to be formed is BATHORHOPSIN in psec after light falls
- Followed by formation of LUMINORHODOPSIN in nsec
- Leads to formation of METARHODOPSIN-I in μsec
- Followed by formation of METARHODOPSIN-II in msec
- Then in seconds is converted into SCOTOPSIN and 11 cis retinal
- It takes minutes to recompose Rhodopsin
- For synthesis retinal must be converted to trans form(occurs in DARK)
Food sources of Vitamin A
- Carrots
- Sweet potatoes
- Green leafy vegetables
- Cantaloupe
- Fish
- Dried apricots
Role of Vitamin A
- all trans retinol, one of the source of Vitamin A
- all trans retinol is converted to all trans retinal
- all trans retinol is converted to 11 cis retinol
- Then it is converted to 11 cis retinal
- Isomerase enzyme plays a role in conversion
- Finally binds with scotopsin
- Vitamin A is present in cytoplasm of rods and in the pigment layer of
retina - Readily available for synthesis of retinal
- Excess retinal is re-converted into vitamin A
- Decreasing light sensitive pigment
- Will be elaborated in light and dark adaptation
Night Blindness
- Occurs with severe vitamin A deficiency
- Synthesis of rhodopsin is reduced
- For night blindness to occur vitamin a–deficient diet for months
- Large quantities of vitamin A is stored in liver
- Reversed in less than 1 hour by intravenous injection of vitamin A
